Biodiversity and Conservation - Online Test
Q1. Match the following:
state
a) Andhra Pradesh
b) Gujarat
c) Sikkim
d) Karnataka
sanctuary
i) Barsey rhododendron sanctuary
ii) Dandeli wildlife sanctuary
iii) Manjira wildlife sanctuary
iv) Sansagir wildlife sanctuary
state
a) Andhra Pradesh
b) Gujarat
c) Sikkim
d) Karnataka
sanctuary
i) Barsey rhododendron sanctuary
ii) Dandeli wildlife sanctuary
iii) Manjira wildlife sanctuary
iv) Sansagir wildlife sanctuary
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
- Manjira wildlife sanctuary Located across the Manjira River, this wildlife sanctuary is situated in the Medak district in Andhra Pradesh (Now in Telangana).
- Also known as Sasan-Gir, or Gir forest, this is a forest and wildlife sanctuary in Gujarat, established in 1965.
- The Varsey Rhododendron Sanctuary or Barsey Rhododendron Sanctuary occupies 104 km² in the Singalila Range in western Sikkim. It borders on Nepal to the west, and on the state of West Bengal to the south across the Rambong Khola stream.
- Dandeli Wildlife Sanctuary is the second largest sanctuary in Karnataka.
Q2. Which of the following are also called lungs of our planet?
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
The Amazon in South America is the largest, most diverse tropical rainforest on Earth, covering an area of five and a half million square kilometres.
The Amazon rainforest functions as a giant air machine that absorbs a large amount of carbon dioxide, and produces oxygen. That is why it is often called the "Lungs of the Earth.
Q3. The newest addition to India’s national parks is:
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Located in the Himalayan foothills, it is contiguous with the Royal Manas National Park in Bhutan. The park is known for its rare and endangered endemic wildlife such as the Assam roofed turtle, hispid hare, golden langur and pygmy hog. It is established in 1990.
Q4. UNESCO launched biosphere reserve programme under its MAB in :
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
Launched in 1971, UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB) is an intergovernmental scientific programme that aims to establish a scientific basis for the improvement of relationships between people and their environment and to protects the endangered species in natural habitat.
Q5. In which of the following protected areas land patches will be permitted for grazing, plantation and cultivation?
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
Biosphere reserve is generally a vast protected area of land patches divided into three zone, core, buffer and transition zone. A transition zone May contain a variety of agricultural activities, grazing, plantation cultivation And settlements and other uses and in which local communities, management agencies, scientists, non-governmental organizations, cultural groups, economic interests and other stakeholders work together to manage and sustainably.
Q6. Diversity can be promoted by:
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
The species that predominates in an ecological community, particularly when they are most numerous or form the bulk of the biomass.
Diversity can be promoted by dominant species. Dominant species of an ecosystem determine the way of diversity which may be linear or diverse.
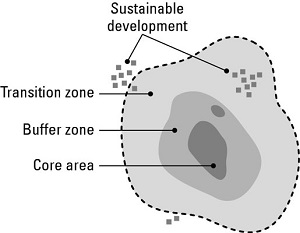
Q7.
If the outermost circle in the shown figure indicates manipulative zone of biosphere reserve then 1& 2 represent:
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
Biosphere reserves are divided into a number of zone. The outer most circle of biosphere represent manipulative zone followed by buffer zone and core zone respectively from outside to inside.
Q8. Sanctuaries, national parks & biosphere reserves are examples of :
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
In situ conservation is the conservation of organisms in their natural geographic regions by providing protection from poaching, cutting or other similar activities. In sanctuaries, national parks and biosphere reserves organisms are kept in natural habitat.
Q9. Humans have increased extinction rate by a factor of
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Various human activities like pollution, deforestation, urbanization, industrialization have increased the extinction rate of various organisms by a factor of 1000.
Q10. Nowadays,the greatest cause for extinction or biodiversity loss is
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
The greatest cause for extinction or biodiversity loss is the habit alteration. Deforestation causes loss of habits of a number of wild animals. Pollution of water also alter the habitat of aquatic organisms.
