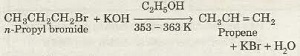Alcohols Phenols and Ethers - Online Test
Give IUPAC name of the compound given below.

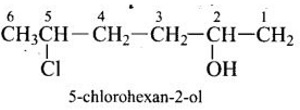
-OH is given preference over -Cl so numbering is done so that –OH gets the lowest number.
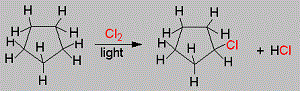
A hydrocarbon C5H10 does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro compound C5H9Cl in bright sunlight. The hydrocarbon is
Cyclopentane is nearly inert chemically, they react with halogens in the presence of light through the substitution of one hydrogen atoms. Since the cyclic structure confers a high degree of symmetry on the molecule, only one monochloro cyclopentane is possible.
Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.

B will be most acidic because of –M effect of NO2 . Followed by d, in d –I effect of NO2 operates only. Then c will come as –I of OCH3 < - I of NO2 and least will be e because of +M effect of OCH3 that will decrease the acidity
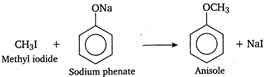
The
reaction of alkyi halide with sodium alkoxide to give ether (alkoxy
alkane), is known as Williamsons synthesis. In this reaction an ether
(anisole) is prepared by the action of alkyi halide (methyl iodide) on
sodium alkoxide (sodium phenate), so it is an example of Williamsons
synthesis.
Alkenes can be prepared from alkyl halides by treatment with alcoholic solution of caustic potash (KOH) at about 353-363 K. This reaction is known as dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides.