Alcohols Phenols and Ethers - Online Test
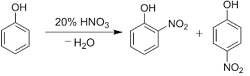
Nitration of phenols: Phenols upon treatment with dilute nitric acid undergoes nitration at low temperature (298 K) to give a mixture of ortho and para nitrophenols. The mixture formed is further separated into ortho and para nitrophenols by steam distillation on the basis of their volatility. Due to intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonding, ortho nitrophenols are lesser volatile in comparison to para nitrophenols which involves only intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
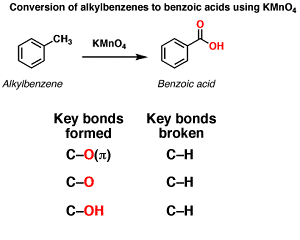
Oxidation of aromatic alkanes with KMnO4 to give carboxylic acids. Description: Treatment of an alkylbenzene with potassium permanganate results in oxidation to give the benzoic acid.
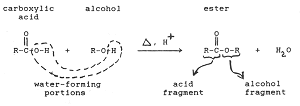
Esterification is the reaction in which a Carboxylic acid combines with an alcohol in the presence of little concentrated sulphuric acid to form an ester. The esters so formed are pleasant smelling.
The addition of water to an alkene in the presence of a catalytic amount of strong acid leads to the formation of alcohols (hydroxy‐alkanes).
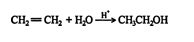
This reaction proceeds via a standard carbocation mechanism and follows the Markovnikov rule.
The mechanism for the addition of water to ethene follows.
1. The hydrogen ion is attracted to the π bond, which breaks to form a σ bond with one of the double‐ bonded carbons. The second carbon of the original double‐bonded carbons becomes a carbocation.
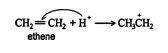
2.An acid‐base reaction occurs between the water molecule and the carbocation, forming an oxonium ion.
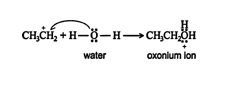
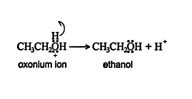
3. The oxonium ion stabilizes by losing a hydrogen ion, with the resulting formation of an alcohol.
What is the correct order of reactivity of alcohols in the following reaction?

The mixture of HCl and ZnCl2 is called the Lucas Reagent. Secondary and tertiary alcohols react via the SN1 mechanism with the Lucas reagent. The ZnCl2 coordinates to the hydroxyl oxygen, and this generates a far superior leaving group.
When alcohols react with a hydrogen halide, a substitution occurs, producing an alkyl halide and water:
Scope of Reaction: The order of reactivity of alcohols is 3° > 2° > 1°
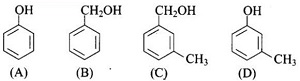
Which of the following compounds is aromatic alcohol?