Alcohols Phenols and Ethers - Online Test

Glycerol and trihydroxypropane are common names. The IUPAC name is propane-1,2,3-triol. The common name glycerol comes from the root glyco- which means sweet. Glucose, glycogen, and glycerin (another name for glycerol) have the same etymology.

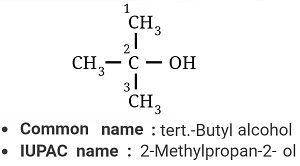
Give IUPAC names of the following compound:
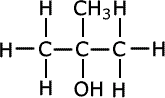
Longest chain has three carbons and at 2nd position both –OH and –CH3 group are attachted.

Anisole, or methoxybenzene, is an organic compound with the formula
C6H5OCH2CH3 is ethyl phenyl ether or phenetole is an organic compound that is an ether. Ethyl phenyl ether has the same properties as some other ethers, such as volatility, explosive vapors, and the ability to form peroxides.
IUPAC name : Ethoxybenzene
Other names : Phenetole, Ethyl Phenyl Ether

Meta-Cresol (m-cresol) also 3-methylphenol, is an organic compound with the formula
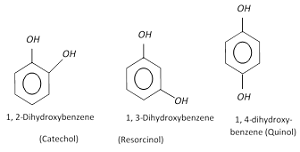
- Catechol is o- hydroxyl phenol or Catechol also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2- dihydroxybenzene,
- Resorcinol is m- hydroxyphenol
- Quinol is p-hydroxyphenol or benzene-1,4-diol is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, a derivative of benzene.
The Grignard Reaction is the addition of an organomagnesium halide (Grignard reagent) to a ketone or aldehyde, to form a tertiary or secondary alcohol, respectively. The reaction with formaldehyde leads to a primary alcohol.
Grignard Reagents are also used in the following important reactions: The addition of an excess of a Grignard reagent to an ester or lactone gives a tertiary alcohol in which two alkyl groups are the same, and the addition of a Grignard reagent to a nitrile produces an unsymmetrical ketone via a metalloimine intermediate.

The Grignard Reaction is the addition of an organomagnesium halide (Grignard reagent) to a ketone or aldehyde, to form a tertiary or secondary alcohol, respectively. The reaction with formaldehyde leads to a primary alcohol.
Grignard Reagents are also used in the following important reactions: The addition of an excess of a Grignard reagent to an ester or lactone gives a tertiary alcohol in which two alkyl groups are the same, and the addition of a Grignard reagent to a nitrile produces an unsymmetrical ketone via a metalloimine intermediate.

